By Valerie Volcovici
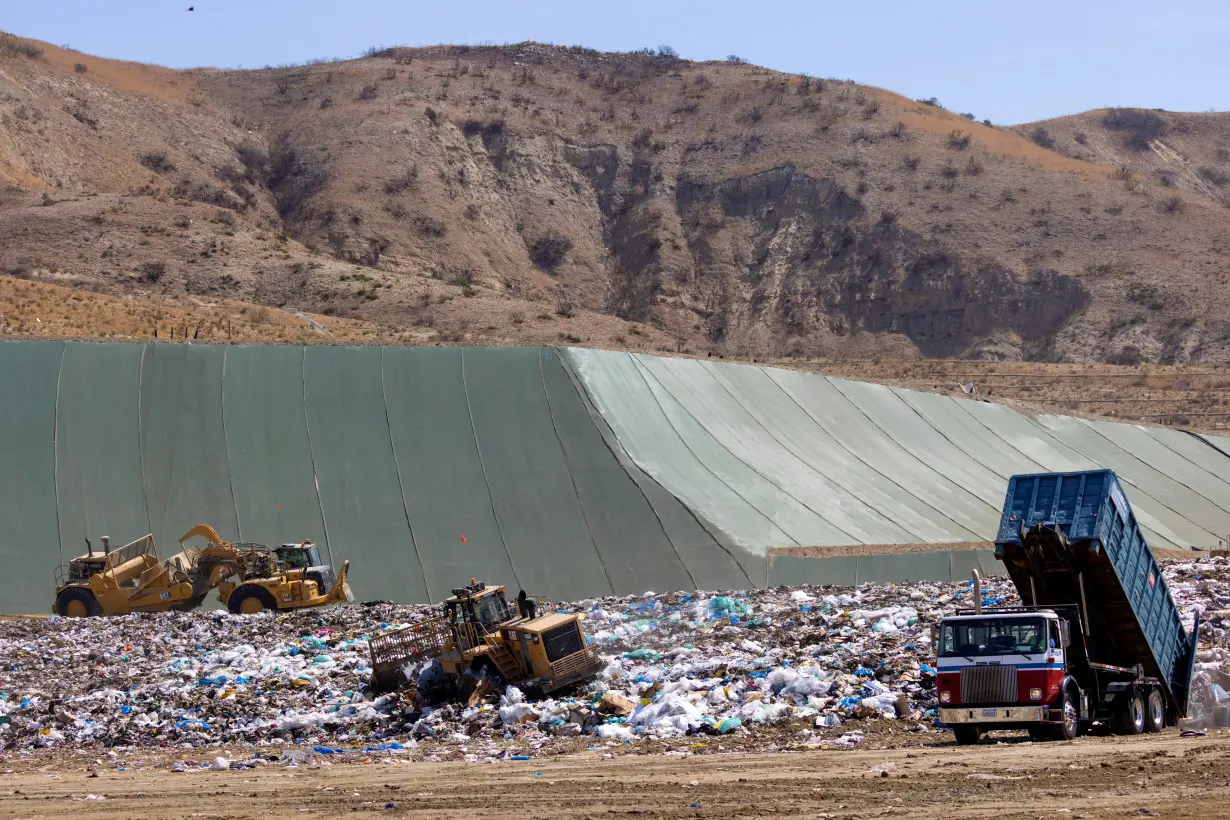
WASHINGTON (Reuters) - Over half of U.S. landfills observed by aerial surveys are super-emitting sources of methane, according to a new study in the journal Science published on Thursday.
The study is the largest assessment to date of methane from landfills, the third-largest source of U.S. methane emissions, and suggests an opportunity to tackle climate change by targeting a prevalent and potent greenhouse gas.
It was led by research group Carbon Mapper, with researchers from NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Arizona State University, University of Arizona, Scientific Aviation, and the Environmental Protection Agency.
Around 52% of landfills had observable methane emission point sources compared to the 0.2% to 1% of "super-emitter" sites in the oil and gas sector, the largest U.S. source of methane.
Super emitters are sources that spew at least 100 kilograms (100 lbs) of methane per hour, according to the EPA.
At large emitting landfills, 60% had methane leaks that persisted over months or years while the majority of leaks at super-emitting sites in the oil and gas sector were "short-duration events," the study said.
Dan Cusworth, scientist at Carbon Mapper and lead author of the study, said that pinpointing these leaks offers a quick way to target emissions.
“Addressing these high methane sources and mitigating persistent landfill emissions offers a strong potential for climate benefit,” he said in a statement.
So far, oil and gas has been the main target of emerging regulations and voluntary programs in the United States, Europe and elsewhere.
But as more aerial and satellite surveys are launched, regulators will be able to measure, quantify and act on methane from landfills.
To date, companies and regulators have relied on model-based estimates of landfill emissions, as well as surveys with handheld methane sensors, which provide a less complete picture, the study said.
The EPA's own greenhouse gas reporting system has underestimated the scale of methane leaks in landfills, according to the study. Aerial surveys showed emission rates were 1.4 times higher than the EPA's estimates.
The EPA said that in 2021, 12% of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions from human activities came from methane.
(Reporting by Valerie Volcovici; Editing by Stephen Coates)